Austrian Nico Wiener Takes on the Best at World Cup Archery Championship
Nico Wiener, a rising star in archery, celebrated with a fist pump after securing a better 10 in his quarter-final tie-break against reigning World Cup archery champion Matthias Fullerton. The…
Surviving the Triple Threat: Navigating Supply Chain Challenges in a Rapidly Changing Business Landscape
Supply chains today face a multitude of challenges, including labor shortages and rising labor costs. In addition to these issues, there is a shift in customer expectations that is commonly…
From the Diamond to the Interview: Luke Suess’s Triumphant Performance and Unique Personality Traits
Luke Suess played a significant role in New Ulm baseball’s victory over Worthington on Saturday. In the two games, he had three hits, four RBIs, and scored two runs each.…
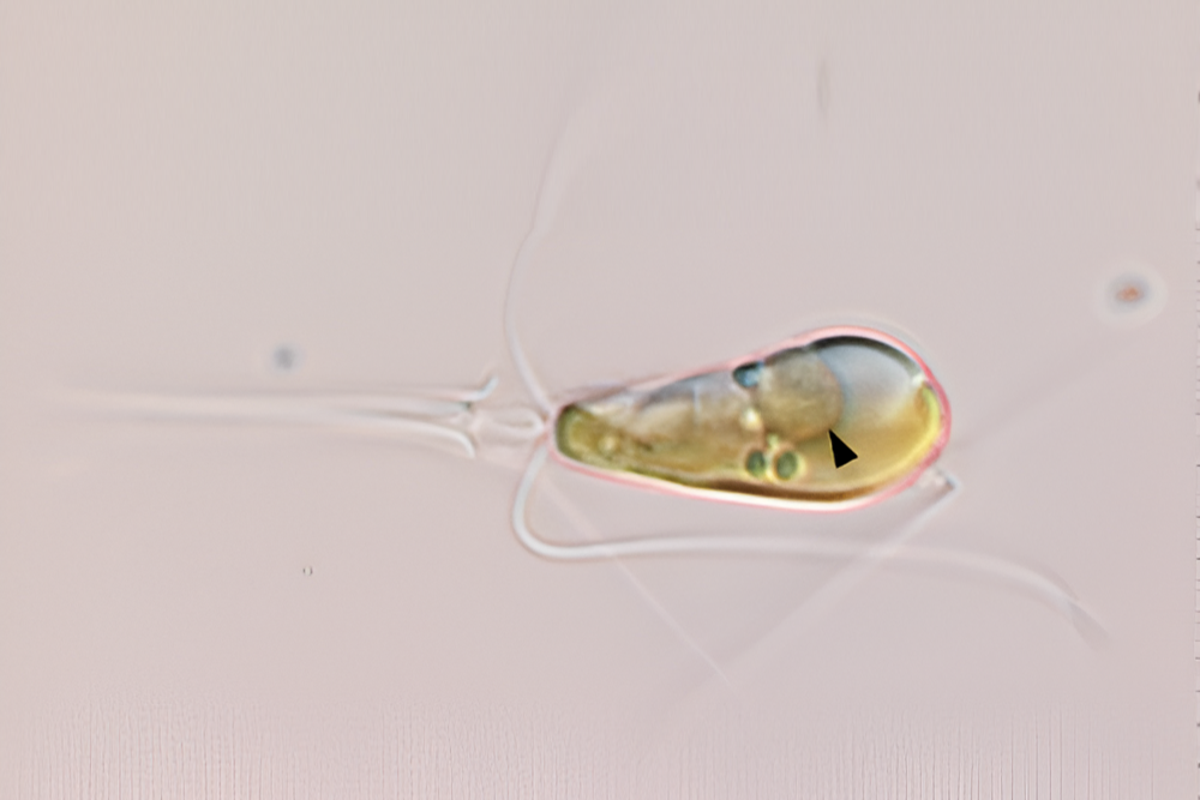
A Revolutionary Discovery: The Unique Symbiosis of Algae and Bacteria Leads to the Emergence of Mitochondria and Plants
Discover the incredible evolutionary event of primary endosymbiosis where two life forms have merged into one organism. This rare occurrence has only happened twice in Earth’s history, resulting in the…
Jessica Culver’s Journey: Grosvenor Teacher Fellowship Takes Her to Alaska’s Wilderness
Jessica Culver, a PhD student in the Adult and Lifelong Learning Program in the Faculty of Education and Health Professions, has been chosen to take part in the Grosvenor Teacher…
Preparing for the Future: Navigating Technological Advancements, Energy Transitions and Population Changes in Texas’ Job Market
The Lone Star State is currently experiencing steady growth, with over 15 million employed Texans. However, the future of work in Texas remains uncertain as technological advancements and climate change…
Transforming Homes on a Budget: FunCicled’s Kitchen Makeover Solutions
FunCicled is a local family business that started as a flipping company in Winnantskill in 2021. They have since expanded their services to include kitchen cabinet painting and interior design.…
Savoring the Sweetness: The World’s Largest Fish Festival in Paris, Tennessee
The 71st annual World’s Largest Fish in Henry County, Tennessee returned to Paris on April 20th, with the opening of the Fish Tent on April 24th. This event is a…
Align Technology Exceeds Expectations with Strong Financial Results, Key Metrics Indicate Continued Success
Align Technology ( ALGN ) has reported strong financial results for the quarter ended March 2024, with revenue of $997.43 million, up 5.8% compared to the same period last year.…
Record-Breaking Sports Travel Spending in 2023: The State of the Industry and Its Impact on Various Sectors
In 2023, the sports travel sector is expected to experience a total direct spending of $52.2 billion, with Americans taking a record 204.9 million trips related to sporting events. The…

-(1).jpg?height=635&t=1713977323&width=1200)